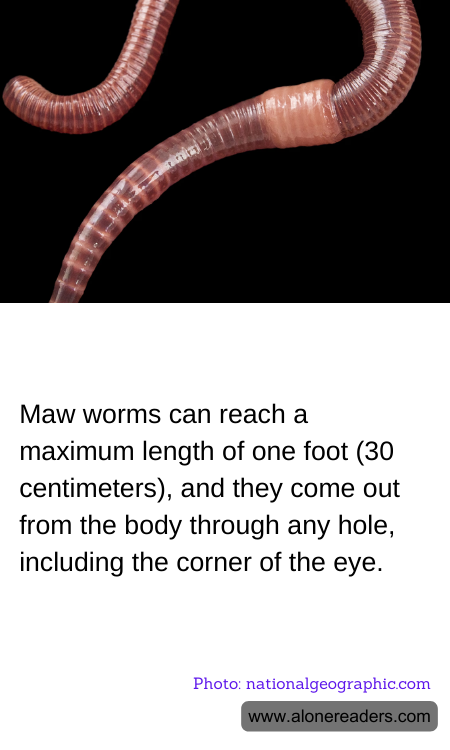
Maw worms, scientifically known as Ascaris lumbricoides, are a type of parasitic roundworm that can inhabit the human body. These worms are notorious for their ability to grow up to one foot (30 centimeters) in length, making them one of the largest intestinal parasites affecting humans. Their presence in the body can lead to a range of health issues, and their migration through the body can be particularly unsettling.
These worms typically enter the human body through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. Once inside, they hatch in the intestines and begin their life cycle. The larvae can penetrate the intestinal wall and travel through the bloodstream to the lungs. From there, they are coughed up and swallowed, returning to the intestines where they mature into adult worms. This journey through the body is not only complex but also potentially harmful, as it can cause a variety of symptoms including abdominal pain, malnutrition, and respiratory issues.
One of the most alarming aspects of maw worms is their ability to exit the body through various orifices. While they primarily reside in the intestines, they can sometimes be expelled through the mouth, nose, or even the corner of the eye. This occurs when the worms become disoriented or when the body attempts to expel them due to an immune response. Such occurrences, although rare, can be distressing and highlight the importance of addressing parasitic infections promptly.
Preventing maw worm infections involves maintaining good hygiene practices. Washing hands thoroughly with soap and water before meals and after using the restroom is crucial. Additionally, ensuring that food is cooked properly and that drinking water is clean can significantly reduce the risk of infection. In areas where these parasites are common, regular deworming treatments may be recommended, especially for children who are more susceptible to infections.
Treatment for maw worm infections typically involves the use of antiparasitic medications, which are effective in eliminating the worms from the body. These medications work by either paralyzing the worms or disrupting their metabolic processes, allowing the body to expel them naturally. In severe cases, where the worms cause blockages or other complications, medical intervention may be necessary.
In conclusion, while maw worms can be a daunting presence due to their size and potential to migrate through the body, understanding their life cycle and taking preventive measures can help mitigate the risks they pose. Awareness and education about these parasites are essential in reducing their impact on human health, ensuring that individuals can lead healthy, worm-free lives.