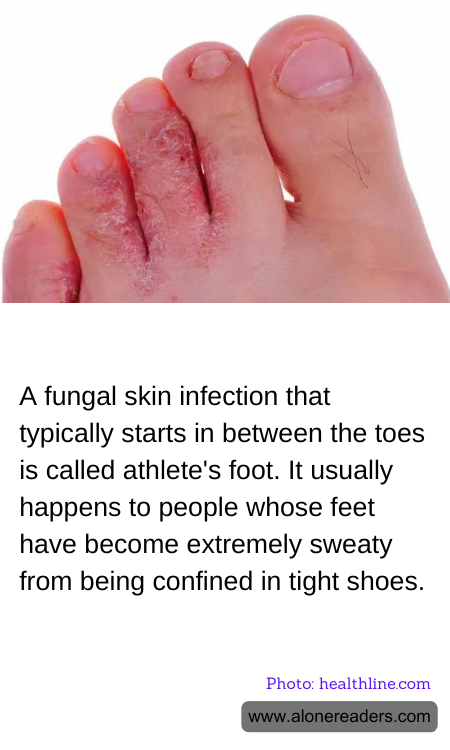
Athlete's foot, medically known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that primarily affects the skin between the toes. This condition is particularly prevalent among individuals whose feet become excessively sweaty, often due to being enclosed in tight-fitting shoes for extended periods. The warm, moist environment created by such footwear provides an ideal breeding ground for the fungi responsible for this infection.
The symptoms of athlete's foot can vary, but they typically include itching, stinging, and burning sensations between the toes. The skin may appear red, scaly, and cracked, and in more severe cases, blisters can form. While the infection commonly starts between the toes, it can spread to the soles of the feet and even to the toenails if left untreated. In some instances, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the hands, if the individual scratches the affected area and then touches other skin surfaces.
Athlete's foot is caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm, damp environments. These fungi are highly contagious and can be contracted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching surfaces contaminated with the fungi, such as floors in communal showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools. Sharing towels, socks, or shoes with an infected person can also lead to the spread of the infection.
Preventing athlete's foot involves maintaining good foot hygiene and taking measures to keep the feet dry and clean. It is advisable to wash the feet daily with soap and water, ensuring they are thoroughly dried, especially between the toes. Wearing breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks can help reduce sweat accumulation. Additionally, changing socks regularly and allowing shoes to air out between uses can minimize the risk of infection. In communal areas, wearing flip-flops or shower shoes can provide a protective barrier against the fungi.
Treatment for athlete's foot typically involves the use of over-the-counter antifungal creams, sprays, or powders. These products are designed to eliminate the fungi and alleviate symptoms. In more persistent cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe stronger antifungal medications. It is crucial to complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated and to prevent recurrence.
While athlete's foot is generally not a serious condition, it can be uncomfortable and inconvenient. By understanding the causes and taking preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this common fungal infection. For those who do experience symptoms, prompt treatment can help restore healthy skin and prevent the spread of the infection to others.