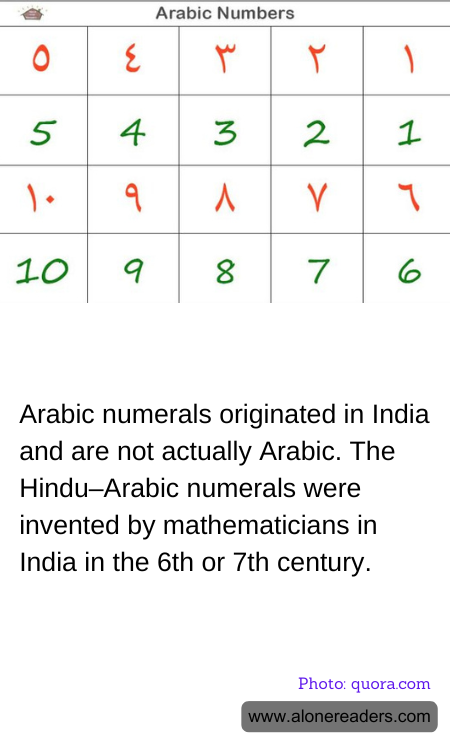
The numerals that we commonly refer to as "Arabic numerals" are, in fact, a remarkable testament to the rich tapestry of human history and cultural exchange. These numerals, which include the familiar digits 0 through 9, have become the universal language of numbers, transcending linguistic and cultural barriers. However, their origins are not rooted in the Arab world as their name might suggest, but rather in ancient India.
The story of these numerals begins in India during the 6th or 7th century. Indian mathematicians, who were at the forefront of mathematical innovation at the time, developed a numeral system that was both efficient and revolutionary. This system included the concept of zero, a groundbreaking development that allowed for more complex calculations and laid the foundation for modern mathematics. The Indian numeral system was based on a decimal structure, which made it highly adaptable and easy to use.
The journey of these numerals from India to the rest of the world is a fascinating tale of cultural exchange. As trade routes expanded and civilizations interacted, the numeral system traveled westward. It was through the Arab scholars and traders that the numerals reached the Islamic world. The Arabs, recognizing the system's superiority over the Roman numerals they were using, adopted and adapted it. They played a crucial role in preserving and disseminating this knowledge, translating Indian mathematical texts into Arabic and further developing mathematical concepts.
By the 10th century, the numerals had made their way to Europe through translations of Arabic mathematical works. European scholars, particularly those in Spain and Italy, began to recognize the advantages of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system over the cumbersome Roman numerals. The system's simplicity and efficiency in calculations led to its gradual adoption across the continent. By the 15th century, the numerals had become widely used in Europe, paving the way for advancements in science, engineering, and commerce.
The misnomer "Arabic numerals" is a reflection of the historical path these numerals took rather than their true origin. While the Arabs were instrumental in introducing these numerals to the Western world, the foundational work was done by Indian mathematicians. This highlights the interconnectedness of human knowledge and the way ideas evolve and spread across cultures.
Today, the Hindu–Arabic numeral system is a global standard, used in virtually every country and in every field of study. It serves as a reminder of the shared heritage of human civilization and the power of cultural exchange in advancing knowledge. Understanding the true origins of these numerals not only enriches our appreciation of history but also underscores the importance of acknowledging and celebrating the contributions of diverse cultures to the collective progress of humanity.