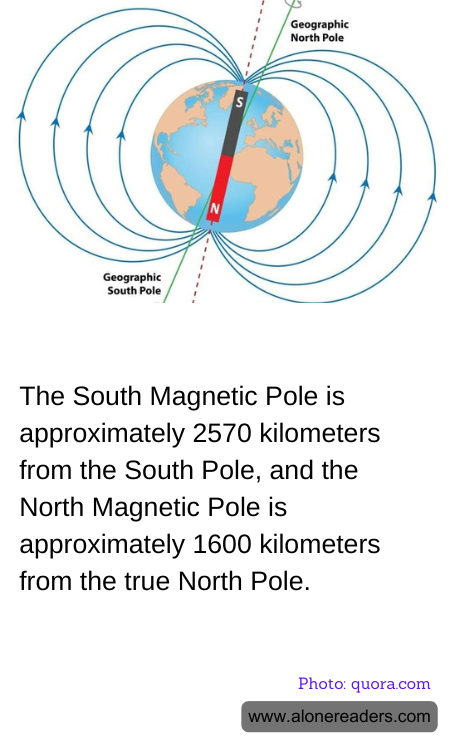
The Earth's magnetic poles are fascinating features that have intrigued scientists and explorers for centuries. Unlike the geographic poles, which are fixed points on the Earth's surface, the magnetic poles are constantly shifting due to changes in the Earth's magnetic field. Currently, the South Magnetic Pole is approximately 2,570 kilometers away from the geographic South Pole, while the North Magnetic Pole is about 1,600 kilometers from the true North Pole. This discrepancy between the magnetic and geographic poles is a result of the complex and dynamic nature of the Earth's interior.
The Earth's magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron and other metals in its outer core. This movement creates electric currents, which in turn produce magnetic fields. These fields combine to form the planet's overall magnetic field, which is not perfectly aligned with the Earth's rotational axis. As a result, the magnetic poles are not located at the same points as the geographic poles. The South Magnetic Pole, for instance, is currently located off the coast of Antarctica, while the North Magnetic Pole is situated in the Arctic Ocean, north of Canada.
The movement of the magnetic poles is a natural phenomenon that has been occurring for millions of years. The poles can shift by several kilometers each year, and their paths are not predictable. This movement is part of a larger process known as geomagnetic secular variation, which involves changes in the Earth's magnetic field over time. These changes can have significant implications for navigation, as compasses point toward the magnetic poles rather than the geographic ones. As the poles move, navigational charts and systems must be updated to ensure accuracy.
Understanding the behavior of the magnetic poles is crucial for various fields, including navigation, geology, and space science. For navigators, especially those operating in polar regions, knowing the location of the magnetic poles is essential for accurate compass readings. In geology, studying the movement of the poles can provide insights into the processes occurring within the Earth's core. Additionally, the Earth's magnetic field plays a vital role in protecting the planet from solar radiation, making it a key area of study for space scientists.
The shifting of the magnetic poles is a reminder of the dynamic nature of our planet. While the geographic poles remain constant, the magnetic poles are in a state of perpetual motion, influenced by the complex interactions within the Earth's core. As scientists continue to study these phenomena, they gain a deeper understanding of the forces shaping our world and the challenges they present for navigation and other human activities. The ongoing research into the Earth's magnetic field not only enhances our knowledge of the planet but also helps ensure the safety and accuracy of navigation systems used by people around the globe.