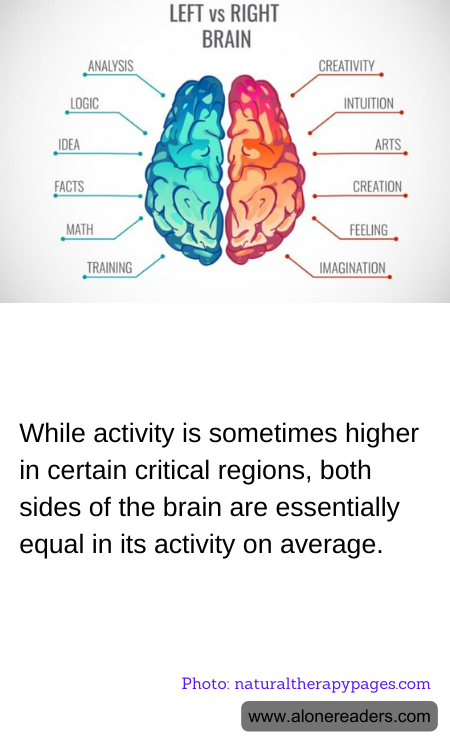
The human brain is a complex and dynamic organ, renowned for its intricate structure and vast capabilities. One of the longstanding myths about the brain is the idea of left-brained or right-brained dominance, which suggests that people are either logical and analytical if they are left-brained, or creative and emotional if they are right-brained. However, recent research indicates that this dichotomy is not only overly simplistic but largely incorrect. Neuroscientific studies show that both hemispheres of the brain are involved in nearly all cognitive tasks, and activity is generally balanced across both sides of the brain.
Neuroimaging technologies, such as fMRI and PET scans, have allowed scientists to observe brain activity in real-time. These studies consistently demonstrate that both the left and right hemispheres are engaged in most types of cognitive processes. For instance, language, which has long been considered a function of the left hemisphere, involves the right hemisphere as well, particularly in aspects like intonation and emphasis. Similarly, activities that are traditionally viewed as right-brain functions, such as spatial abilities or facial recognition, also involve the left hemisphere to a significant extent.
The idea of symmetrical brain activity can also be understood through the concept of brain plasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This ability allows the brain to compensate for injury or adapt to new learning experiences by utilizing both hemispheres. For example, if one hemisphere is damaged, the other can often take over some of its functions, further demonstrating the cooperative nature of the two sides of the brain.
Additionally, while certain regions of the brain may show more activity during specific tasks, this does not imply that other regions are inactive. Instead, the human brain operates as a highly interconnected network, with continual communication between both hemispheres. This communication is facilitated by the corpus callosum, a thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres, allowing them to work together harmoniously.
In conclusion, the notion that one hemisphere is more active or significantly more crucial than the other is a misconception. Both hemispheres of the brain contribute equally to who we are, including our thoughts, actions, creativity, and logic. Understanding the cooperative nature of the brain's hemispheres can help debunk stereotypes about personality traits supposedly linked to left-brained or right-brained dominance and provide a more accurate view of human potential and cognitive abilities.