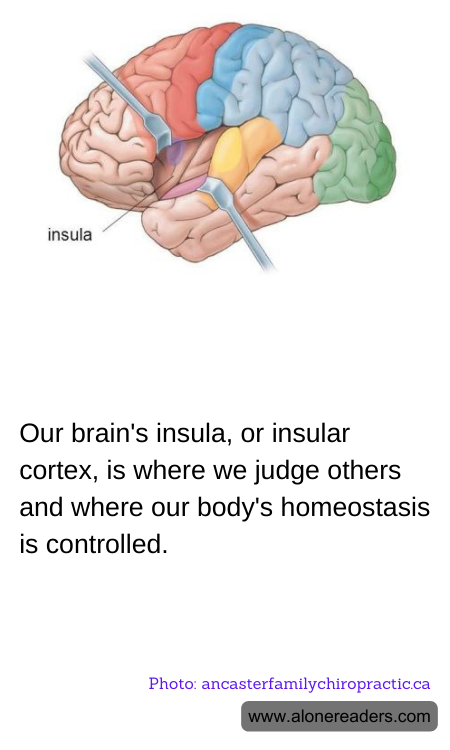
The insula, also known as the insular cortex, is a fascinating and complex part of the human brain, intricately involved in a myriad of our psychological functions. Nestled deep within the lateral sulcus, the insula bridges the gap between our emotional states and cognitive processes. This small region of the brain is responsible for various roles ranging from emotional to homeostatic functions, earning it considerable focus in neuroscience research.
One of the primary functions of the insula is its involvement in the perception and judgment of others. It plays a crucial role in social emotions, which include feelings of empathy, disgust, and fairness. Studies have shown that when we judge the actions or intentions of others, the insula is activated, particularly when those judgments are morally laden. This suggests that the insula may be responsible for triggering emotional responses in situations that require social and moral reasoning, potentially influencing our decisions about what is right or wrong in social contexts.
Moreover, the insula is essential in the management of homeostasis or the body’s internal balance. It integrates various signals from different parts of the body, like heart rate, hunger, pain, and thirst, to help maintain a stable internal environment. By monitoring and interpreting these signals, the insula plays a vital role in regulating our autonomic nervous system, which unconsciously controls bodily functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion.
The connection between how we judge others and how our body maintains homeostasis might seem unclear at first, but there is growing evidence that our social interactions can influence our physical states. For example, experiencing social stress or distress can trigger changes in heart rate and blood pressure, responses mediated by the insula. This shows how intertwined our social behaviors and physiological processes are, with the insula at the core of this interface.
The insular cortex's dual role in processing both external social cues and internal bodily states uniquely positions it as a bridge linking our emotional worlds with our physical health. It underscores a fundamental aspect of human biology: that our social interactions and how we perceive others are not just relegated to thoughts and feelings but are deeply rooted in our biology, affecting how our bodies function.
Given its roles in critical aspects of human experience, the health of the insular cortex is paramount. Disorders of the insula, such as in cases of stroke or neurodegenerative diseases, can profoundly impact a person's capability to empathize with others or regulate their own emotions and bodily functions efficiently. As our understanding of the insula deepens, it may offer new insights into treating psychological and neurological disorders, enhancing our approach to mental and physical health.