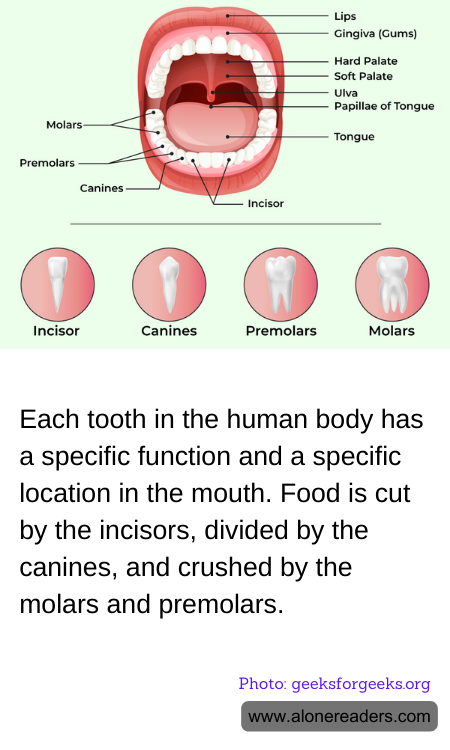
Teeth are essential components of the human body, not only for aesthetic purposes but predominately for facilitating the process of digestion through mastication, or chewing. Each type of tooth has a specialized function and is uniquely adapted to perform specific tasks that aid in the mechanical breakdown of food, making it easier for the digestive system to convert it into energy.
Incisors are the eight front teeth located in the front part of the mouth (four on the top and four on the bottom). These teeth are primarily used for cutting and shearing food into manageable pieces. They have sharp, thin edges that make them perfect for biting into food like apples or cucumbers.
Adjacent to the incisors are the canines, which are four in number – two on the top and two on the bottom. These teeth are also known as cuspids because of their sharp, pointed edges. Canines are designed to tear food, which is why they are much stronger and have a more pointed biting surface compared to incisors. They play a crucial role in eating meat or other tough materials, acting somewhat like the claws of a predator breaking down its prey.
Behind the canines are the premolars, or bicuspids, and molars. Humans typically have eight premolars and eight to twelve molars, depending on whether the wisdom teeth are present. Both premolars and molars are characterized by their broad and flat surfaces designed for grinding and crushing food into smaller, more digestible pieces. This is crucial for the breakdown of tougher food substances like nuts, grains, and vegetables, which require more forceful handling than cutting or tearing.
Overall, the collaboration of incisors, canines, premolars, and molars allows for a comprehensive processing of food, which is essential for effective digestion. Each type of tooth contributes to preparing the food for chemical digestion in the stomach and intestines, underscoring the importance of maintaining dental health not just for a beautiful smile, but also for a well-functioning digestive system. This intricate arrangement not only facilitates the physical breakdown of food but also ensures that each tooth type is positioned for optimal force application during eating, reflecting the sophisticated nature of human anatomy and evolution.