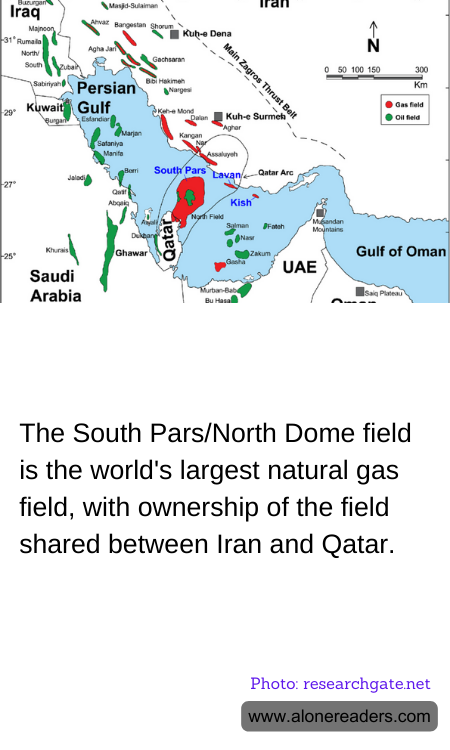
The South Pars/North Dome field, a giant natural gas reservoir beneath the waters of the Persian Gulf, is one of the most significant natural resources currently being extracted. This immense gas field, shared by Iran and Qatar, is recognized as the largest in the world. Spanning around 9,700 square kilometers, with the majority lying in Qatari waters where it is called the North Dome and the remainder in Iranian waters, known as South Pars, it highlights the vast potential and geopolitical importance of natural resources in the region.
The field's significance extends far beyond its size. It holds an estimated 1,800 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, which accounts for nearly 20% of the world’s total reserves. In addition, the field contains condensate reserves which are an important by-product used in the petrol refinery industry. This makes it a crucial asset not just for Iran and Qatar, but also for global energy markets, influencing gas prices and energy policies worldwide.
Iran and Qatar have pursued very different approaches in exploiting the field primarily due to differing economic policies, sanctions, and technological access. Qatar has successfully capitalized on its share with the development of liquefied natural gas (LNG) technologies thanks to collaborations with international oil companies. This has not only bolstered Qatar's economy but also made it one of the leading LNG exporters globally. On the other hand, Iran has faced challenges such as international sanctions that have restricted its ability to fully develop and profit from its portion of the field. Despite these hurdles, Iran has made significant progress in recent years, focusing on boosting domestic infrastructure and capabilities to increase gas production.
The development and management of the South Pars/North Dome field have notable implications for the environment as well. Extracting and processing natural gas, while cleaner than coal or oil in terms of emissions, pose risks including methane leaks and other ecological disturbances. Both countries have faced international scrutiny regarding environmental impacts, pushing them towards adopting more sustainable and environmentally friendly extraction technologies.
In conclusion, the South In conclusion, the South Pars/North Dome field is not only a cornerstone of the Iranian and Qatari economies but also a pivotal element in the energy security strategies of countries around the Persian Gulf and beyond. Its continued development is set to play a key role in shaping global energy supplies and geopolitical dynamics in the coming decades. This underscores the need for sustainable practices and international cooperation to optimize the benefits of such a vast natural resource while mitigating environmental and regional risks.