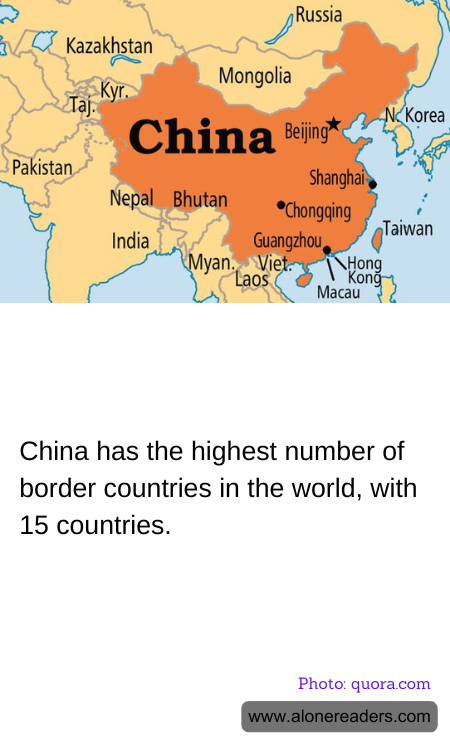
China, a vast and diverse nation, holds the unique distinction of sharing its borders with more countries than any other nation in the world. With a total of 15 neighboring countries, China's extensive land borders stretch across a variety of terrains, from towering mountains to expansive deserts, and encompass a rich tapestry of cultures and histories.
The countries that share a border with China are Afghanistan, Bhutan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan, Vietnam, and the disputed region of Tibet. This geographic positioning places China at a strategic crossroads in Asia, influencing its political, economic, and cultural interactions with its neighbors.
China's border with Russia is the longest, extending over 4,200 kilometers, and is characterized by a history of both cooperation and tension. The two countries have worked together on various economic and security initiatives, yet historical disputes occasionally resurface. Similarly, the border with India, which spans approximately 3,380 kilometers, is another significant frontier. It has been a focal point of geopolitical interest, with both nations striving for regional influence and occasionally experiencing border skirmishes.
The diversity of China's border regions is reflected in the varied relationships it maintains with each neighboring country. For instance, the border with Mongolia is largely peaceful, facilitating trade and cultural exchanges. In contrast, the border with North Korea is more complex, shaped by historical alliances and contemporary geopolitical challenges. The Yalu and Tumen rivers form natural boundaries, and the region is a critical area for monitoring North Korean activities.
China's southern borders with countries like Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar are marked by lush landscapes and vibrant cross-border trade. These regions have seen increased economic collaboration, particularly through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, which aims to enhance connectivity and economic integration across Asia and beyond.
The presence of diverse ethnic groups along China's borders adds another layer of complexity to its relationships. Many of these groups have cultural and familial ties that transcend national boundaries, influencing cross-border interactions. For example, the Tibetan plateau, which borders Nepal, India, and Bhutan, is home to Tibetan communities with deep cultural connections to these neighboring countries.
China's extensive borders present both opportunities and challenges. They offer avenues for economic growth and cultural exchange but also require careful management to maintain stability and security. As China continues to rise as a global power, its relationships with its neighbors will play a crucial role in shaping the geopolitical landscape of the 21st century. The intricate web of interactions along its borders underscores the importance of diplomacy, cooperation, and mutual understanding in fostering peaceful and prosperous relations in the region.