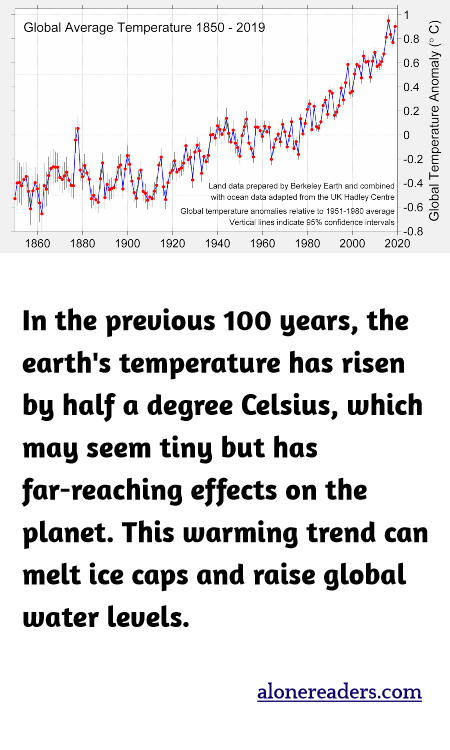
Over the past century, the Earth's average temperature has increased by approximately 0.5 degrees Celsius. While this rise might appear minimal, its implications are profound and far-reaching, affecting various environmental, biological, and climatic systems globally. One of the most visible and concerning impacts of this temperature increase is the melting of ice caps. Polar regions, particularly the Arctic and Antarctic, have exhibited significant ice loss, directly contributing to rising sea levels.
The consequences of shrinking ice caps are multifaceted. Firstly, as ice melts, it leads to higher sea levels, which can cause coastal erosion, increased flooding, and threaten coastal communities and habitats. This not only impacts human settlements but also affects coastal ecosystems that can be delicate and rich in biodiversity. For instance, mangroves, coral reefs, and tidal marshes, which are critical for carbon sequestration and as buffers against storms and hurricanes, are at risk.
Moreover, the loss of ice caps affects planetary albedo — the Earth’s ability to reflect solar radiation back into space. Normally, ice and snow reflect a substantial part of the sunlight, but as they diminish, the darker exposed surfaces of water or land absorb more sunlight, leading to further warming. This feedback loop accelerates global warming, making it a growing concern for climatologists and environmental scientists.
Increasing global temperatures also have broader climatic impacts, such as more intense and frequent extreme weather events, including hurricanes, droughts, heatwaves, and heavy rainfall. These events not only cause immediate environmental damage but also have long-term socio-economic effects on agriculture, water resources, and human health.
The complex interplay between these factors underscores the challenge of addressing global warming. International initiatives like the Paris Agreement aim to cap global temperature rises by significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, the ongoing increase in global temperatures demands enhanced global cooperation and innovative solutions to mitigate environmental, health, and economic risks associated with climate change. As we progress, the need for sustainable practices and proactive adaptation strategies becomes more crucial in safeguarding our planet’s future.