When buying motor insurance, one of the first decisions you’ll face is whether to opt for Comprehensive Insurance or Third-Party Insurance. While both protect you financially after an accident, they differ significantly in coverage scope, cost, and applicability. A basic understanding often isn’t enough—small policy details can make a big difference in your claim experience and out-of-pocket expenses. This article dives deeply into what each type covers, what it doesn’t, and how to decide which is right for you.
Definition and Scope
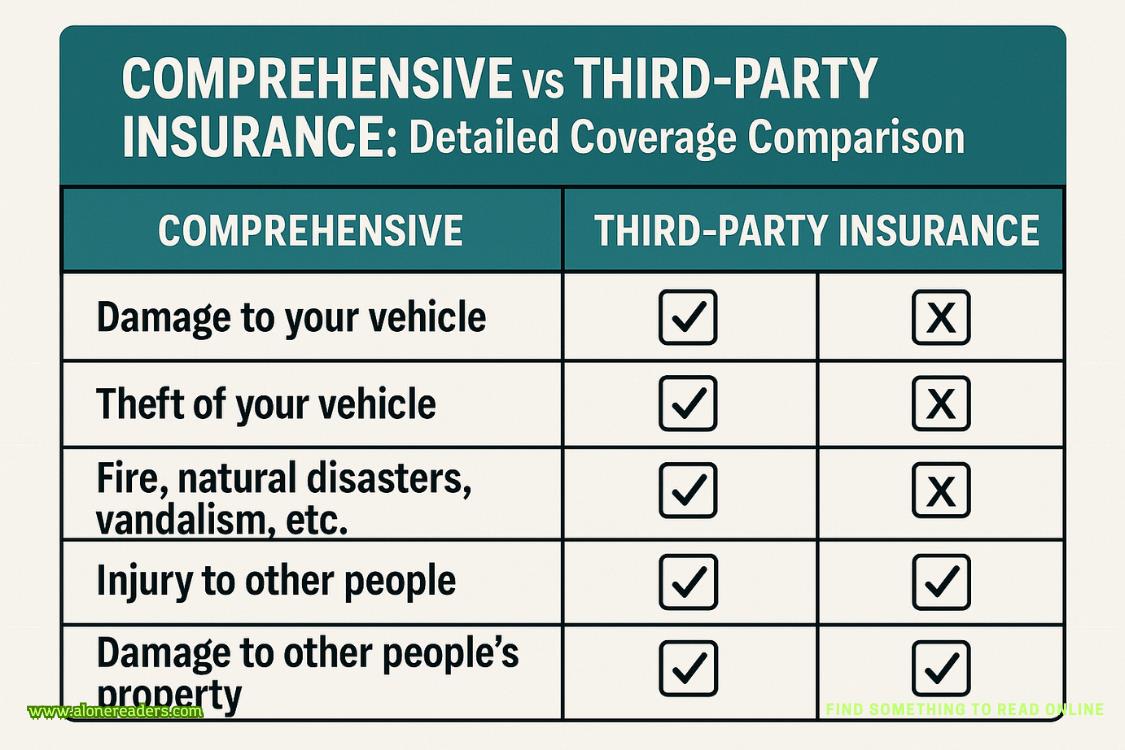
Comprehensive insurance provides the widest coverage available for vehicle owners. It covers damage to your own car, damage to third-party property, and a wide range of non-collision events. This is often referred to as “own damage + third-party” cover.
What It Covers
Key Advantages
Limitations & Exclusions
Definition and Scope
Third-party insurance is the most basic form of legally required motor insurance in many countries. It only covers damage or injury you cause to others, offering no protection for your own vehicle.
What It Covers
What It Does NOT Cover
Key Advantages
Limitations & Exclusions
| Aspect | Comprehensive Insurance | Third-Party Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Own Vehicle Damage | Covered | Not Covered |
| Third-Party Liability | Covered | Covered |
| Theft Protection | Covered | Not Covered |
| Natural Disasters | Covered | Not Covered |
| Fire & Vandalism | Covered | Not Covered |
| Premium Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Customizable Add-ons | Yes | Limited |
| Best For | New/expensive cars, high-risk areas, or high usage | Older/low-value cars or budget-conscious drivers |
Why Comprehensive Costs More
Factors Affecting Premiums for Both Types
Choosing between comprehensive and third-party insurance should not be a decision based purely on price. Comprehensive insurance offers extensive protection, making it ideal for new or high-value vehicles and high-risk driving environments. Third-party insurance, while limited, is a cost-effective option for older cars or those seeking to meet legal requirements at the lowest possible cost.
A good rule of thumb is to weigh the replacement cost of your vehicle against the annual difference in premiums. If your vehicle’s value is significantly higher than the savings from choosing third-party coverage, comprehensive insurance usually makes better long-term sense.